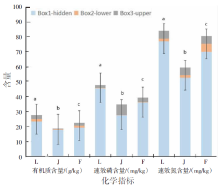
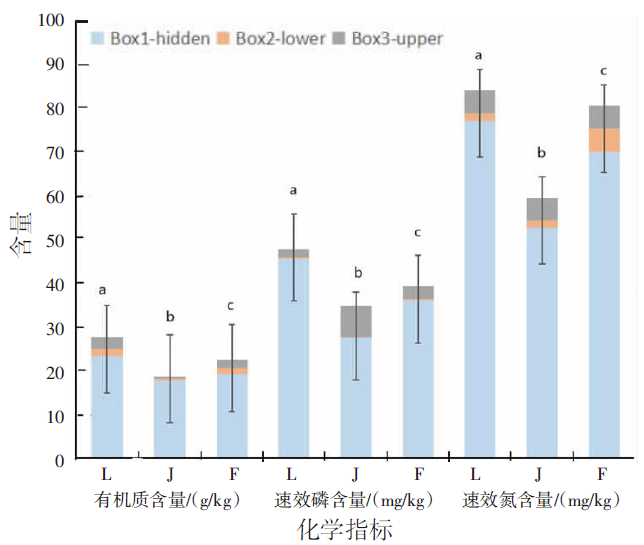
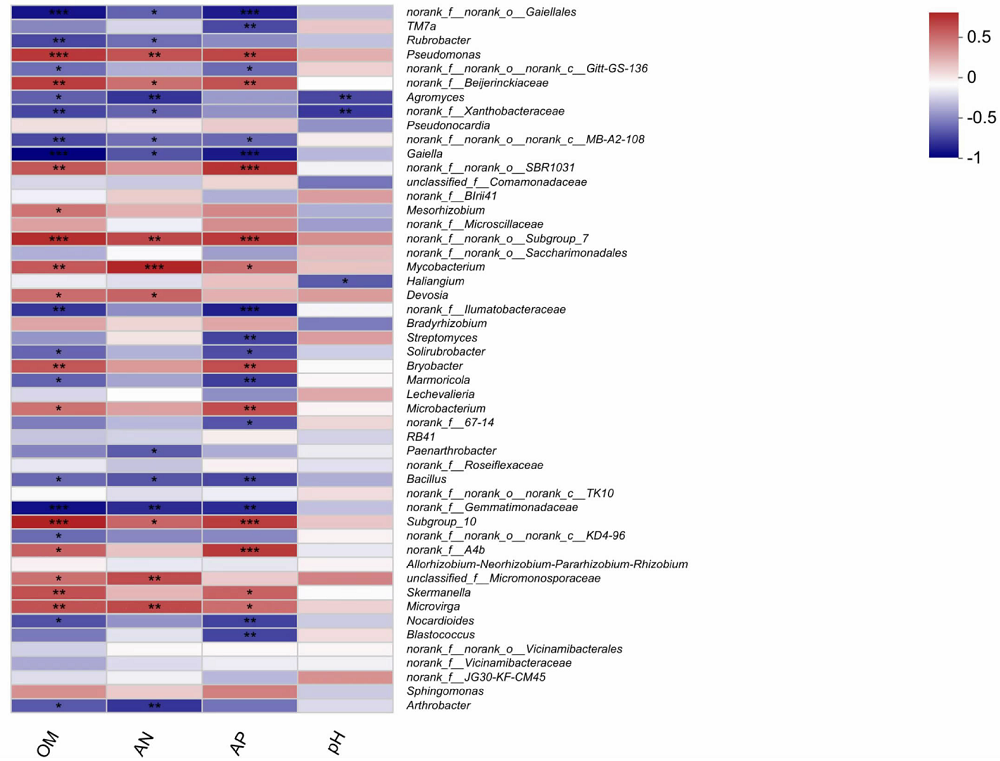
| [1] |
纳小凡, 郑国琦, 彭励, 等. 不同种植年限宁夏枸杞根际微生物多样性变化[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(1):241-252.
|
| [2] |
胡雷, 王长庭, 王根绪, 等. 三江源区不同退化演替阶段高寒草甸土壤酶活性和微生物群落结构的变化[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(3):8-19.
|
| [3] |
赵帅, 张静妮, 赖欣, 等. 放牧与围栏内蒙古针茅草原土壤微生物生物量碳、氮变化及微生物群落结构PLFA分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(6):1126-1134.
|
| [4] |
张向茹. 宁南山区枯落物分解对土壤微生物群落结构及有机碳形态的影响[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2014.
|
| [5] |
王娟娟, 马云, 狄霖, 等. 秸秆还田及配施氮肥对土壤微生物群落结构及铁氧化菌丰度的影响[J]. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2022, 43(1):97-104.
|
| [6] |
徐丽霞. 谷田土壤微生物多样性及对谷子生理生化和产量的影响[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2019.
|
| [7] |
张凯煜, 谷洁, 王小娟, 等. 生物有机肥对核桃园土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2019, 37(6):178-183.
|
| [8] |
谢宝明. 黑麦草和羊草对石油污染盐碱土壤根际微生物的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨师范大学, 2015.
|
| [9] |
李景环. 加拿大披碱草、老芒麦及其杂交后代的遗传分析[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2008.
|
| [10] |
王沛, 陈玖红, 王平, 等. 披碱草属植物抗逆性研究现状和存在的问题[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(5):151-162.
|
| [11] |
严学兵, 周禾, 王堃, 等. 披碱草属植物形态多样性及其主成分分析[J]. 草地学报, 2005, 13(2):111-116.
doi: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2005.02.006
|
| [12] |
陈仕勇. 小麦族披碱草属、鹅观草属六倍体物种分子系统学研究[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2013.
|
| [13] |
刘锦川, 云锦凤. 加拿大披碱草研究进展[J]. 种子, 2011, 30(5):53-57.
|
| [14] |
李景环, 何慧敏, 云锦凤. 加拿大披碱草45S rDNA定位[J]. 华北农学报, 2013, 28(1):67-69.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7091.2013.01.013
|
| [15] |
李景环, 云锦凤, 吕天池, 等. 加拿大披碱草与老芒麦及其杂种后代同工酶和RAPD遗传分析[J]. 华北农学报, 2009, 24(6):38-45.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2009.06.008
|
| [16] |
李景环, 云锦凤, 邰丽华, 等. 加拿大披碱草和老芒麦及其杂种F1,F2的RAPD分析[J]. 华北农学报, 2007, 22(6):77-80.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2007.06.016
|
| [17] |
席娇. 荒漠植物的多功能PGPR的分离鉴定及其功能特性研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2017.
|
| [18] |
唐凯, 贾丽娟, 高晓丹, 等. 浑善达克沙地生物土壤结皮及其下层土壤中好氧不产氧光营养细菌群落结构及多样性[J]. 微生物学报, 2018, 58(2):228-237.
|
| [19] |
李朝英, 郑路. 土壤pH测定的影响因素探讨[J]. 上海农业学报, 2021, 37(1):47-52.
|
| [20] |
鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
|
| [21] |
胡骞予, 蔡永占, 韩小女, 等. 健康与感染黑胫病烟株根际土壤细菌群落结构与多样性[J]. 福建农业学报, 2022, 37(2):233-239.
|
| [22] |
贾丽娟. 生物土壤结皮中解磷微生物群落结构和多样性及其作用研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2019.
|
| [23] |
张春林, 尚晓蕊, 赵鑫, 等. 寒旱区柠条根际细菌群落结构与多样性研究[J]. 北方园艺, 2021(17):97-103.
|
| [24] |
唐凯, 高晓丹, 贾丽娟, 等. 浑善达克沙地生物土壤结皮及其下层土壤中固氮细菌群落结构和多样性[J]. 微生物学通报, 2018, 45(2):293-301.
|
| [25] |
刘艳君, 刘文辉, 祁娟, 等. 不同种植年限老芒麦根际土壤营养与细菌群落多样性[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2020, 38(5):8-14.
|
| [26] |
钟杨权威. 长期施氮对旱作麦田土壤碳库平衡及其稳定性影响机制[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2016.
|
| [27] |
武寒. 云南金平砂仁根际土壤生态环境研究[D]. 昆明: 云南中医学院, 2018.
|
| [28] |
蔡军. 芽孢杆菌LFB112的基因组学及其对鸡肉品质和肠道菌群调控的研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2014.
|
| [29] |
贾若坦. 单级自养脱氮反应器的脱氮特性研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2018.
|
| [30] |
史晓凯. 蓄水坑灌水氮热耦合作用下土壤中氮素转化与微生态环境特征研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2017.
|
| [31] |
VAN WYK D A B, ADELEKE R, RHODE O H J, et al. Ecological guild and enzyme activities of rhizosphere soil microbial communities associated with Bt-maize cultivation under field conditions in North West Province of South Africa[J]. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2017, 57(9):781-792.
doi: 10.1002/jobm.201700043
pmid: 28731210
|
| [32] |
BATISTA É R, CARNEIRO J J, ARAÚJO PINTO F, et al. Environmental drivers of shifts on microbial traits in sites disturbed by a large-scale tailing dam collapse[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 738:139-453.
|
| [33] |
张永亮, 于铁峰, 郝凤. 施肥和混播对人工草地土壤速效养分含量的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(9):88-96.
|
| [34] |
苏贝贝, 张英, 道日娜. 4种豆科栽培牧草根际土壤细菌群落分布特征研究[J]. 草地学报, 2021, 29(2):250-258.
doi: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2021.02.006
|
| [35] |
连文慧, 董雷, 李文均. 土壤环境下的根际微生物和植物互作关系研究进展[J]. 微生物学杂志, 2021, 41(4):74-83.
|
| [36] |
付莉娇, 李雪琴, 范继辉, 等. 藏北高寒草原典型植物根际土壤细菌群落结构多样性及根系特征分析[J]. 草地学报, 2022, 30(5):1131-1140.
doi: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2022.05.013
|
| [37] |
陈孟立, 曾全超, 黄懿梅, 等. 黄土丘陵区退耕还林还草对土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(4):1824-1832.
|
| [38] |
陈海生, 刘守平, 梁国钱, 等. 3种西兰花种植方式对根际土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的影响研究[J]. 核农学报, 2021, 35(6):1457-1465.
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.06.1457
|
| [39] |
袁仁文, 刘琳, 张蕊, 等. 植物根际分泌物与土壤微生物互作关系的机制研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(2):26-35.
|
| [40] |
贾渊. 荒漠草原植物根分泌物及其有机酸组分对土壤中微生物及养分的影响[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2019.
|