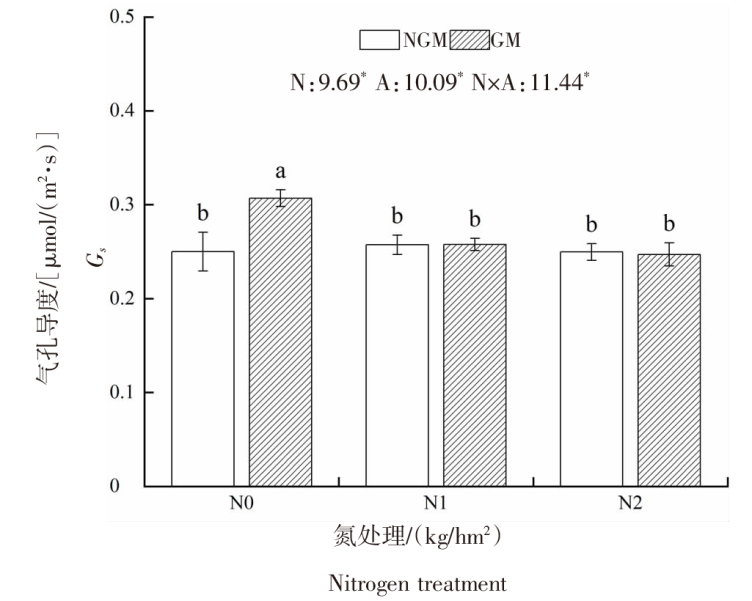
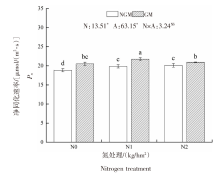
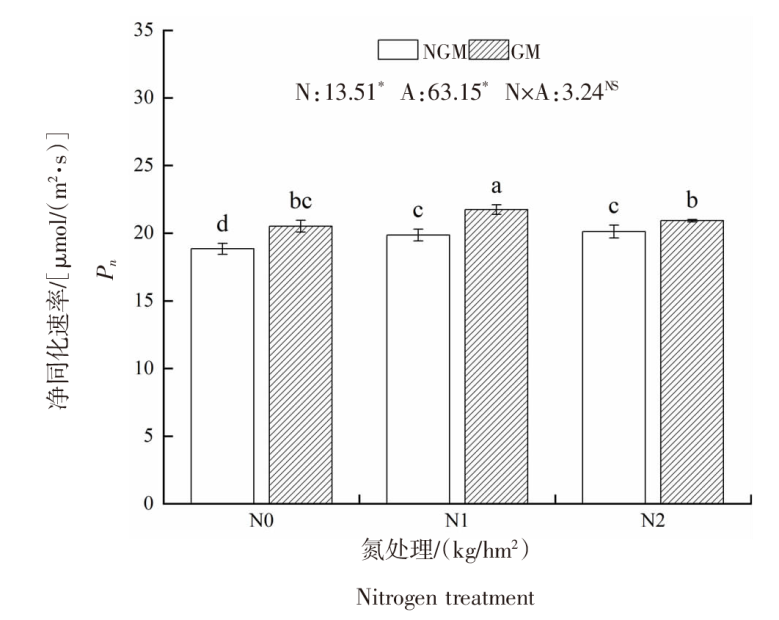
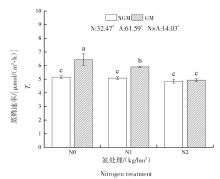
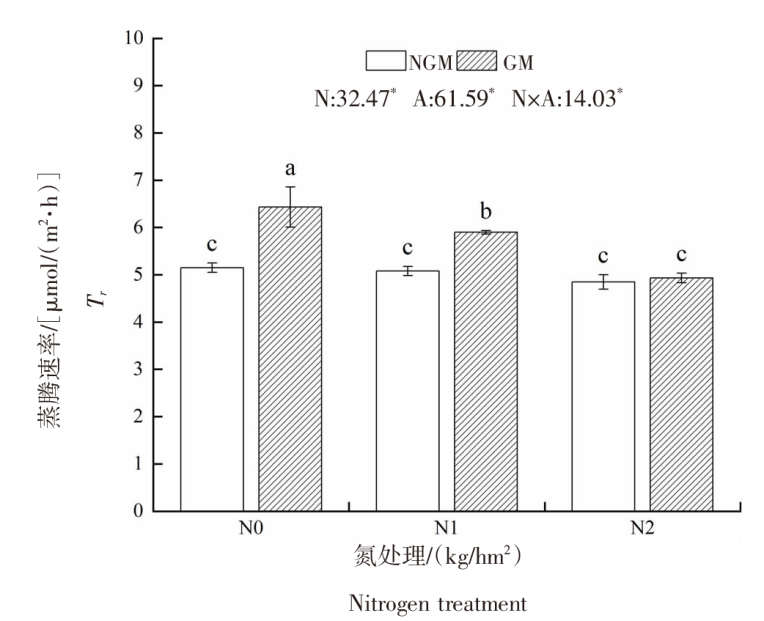
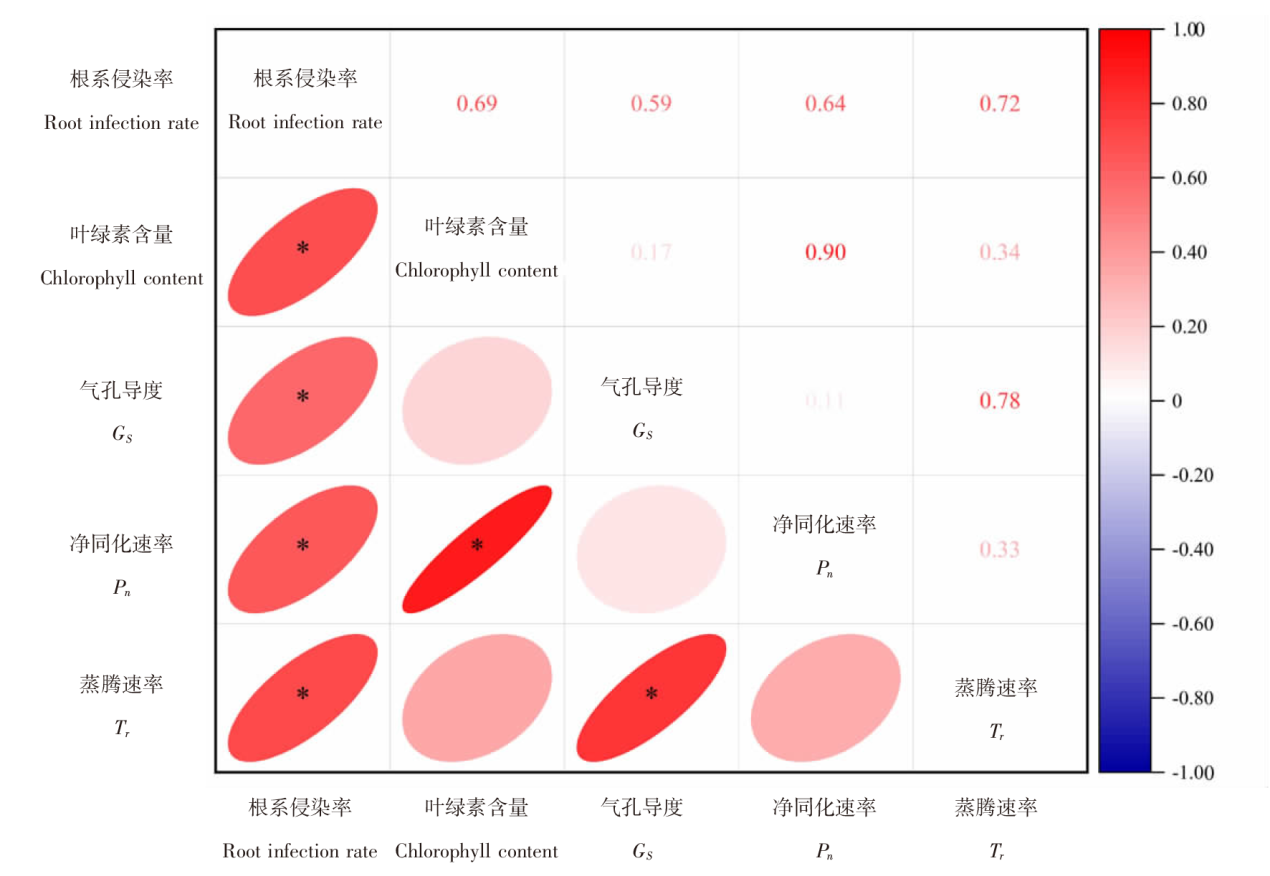
| [1] |
马尚耀, 严福忠, 成慧娟. 高粱的研究现状与展望[J]. 内蒙古农业科技, 2002, 30(6):8-9.
|
| [2] |
ZEGADA-LIZARAZU W, MONTI A. Are we ready to cultivate sweet sorghum as a bioenergy feedstock?A review on field management practices[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2012, 40:1-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.01.048
|
| [3] |
谢光辉, 庄会永, 危文亮. 非粮能源植物:生产原理和边际地栽培[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2011:14-34.
|
| [4] |
于振文. 作物栽培学各论:北方本[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2013.
|
| [5] |
GRÜMBERG B C, URCELAY C, SHROEDER M A, et al. The role of inoculum identity in drought stress mitigation by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in soybean[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 2015, 51(1):1-10.
doi: 10.1007/s00374-014-0942-7
|
| [6] |
WU Q S, XIA R X, ZOU Y N. Improved soil structure and citrus growth after inoculation with three arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under drought stress[J]. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2008, 44(1):122-128.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejsobi.2007.10.001
|
| [7] |
TANAKA Y, YANO K. Nitrogen delivery to maize via mycorrhizal hyphae depends on the form of N supplied[J]. Plant,Cell and Environment, 2005, 28(10):1247-1254.
doi: 10.1111/pce.2005.28.issue-10
|
| [8] |
SHARMA S, SINGH P, CHOUDHARY O P. Nitrogen and rice straw incorporation impact nitrogen use efficiency,soil nitrogen pools and enzyme activity in rice-wheat system in north-western India[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021, 266:108131.
doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108131
|
| [9] |
梁煜, 常翠翠, 郝兴宇, 等. CO2浓度升高与氮素胁迫对谷子光合特性和产量因素的影响[J]. 山西农业科学, 2020, 48(3):401-406.
|
| [10] |
高丽敏, 田倩, 苏晶, 等. 施氮水平对甜高粱干物质产量及氮肥利用率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(4):192-198.
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2019287
|
| [11] |
YAMATO M, IKEDA S, IWASE K. Community of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in a coastal vegetation on Okinawa Island and effect of the isolated fungi on growth of sorghum under salt-treated conditions[J]. Mycorrhiza, 2008, 18(5):241-249.
doi: 10.1007/s00572-008-0177-2
pmid: 18516629
|
| [12] |
LU Y W, LIU X, ZHOU S R. Nitrogen addition altered the plant-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi network through reducing redundant interactions in an alpine meadow[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2022, 171:108727.
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2022.108727
|
| [13] |
VIERHEILIG H, COUGHLAN A P, WYSS U, et al. Ink and vinegar,a simple staining technique for arbuscular-mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1998, 64(12):5004-5007.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.64.12.5004-5007.1998
|
| [14] |
HODGE A, FITTER A H. Substantial nitrogen acquisition by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi from organic material has implications for N cycling[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(31):13754-13759.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005874107
pmid: 20631302
|
| [15] |
WANG J A, YANG C X, SUN X M, et al. Growth responses of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under simulated nitrogen deposition[J]. Bangladesh Journal of Botany, 2021, 50(5):933-938.
|
| [16] |
XUE J H, MO J M, LI J, et al. Effects of nitrogen deposition on ectomycorrhizal fungi[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2004, 24(8):1785-1792.
|
| [17] |
JOHNSON N C. Resource stoichiometry elucidates the structure and function of arbuscular mycorrhizas across scales[J]. New Phytologist, 2010, 185(3):631-647.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03110.x
pmid: 19968797
|
| [18] |
田明慧, 杨硕, 杜嘉琪, 等. 不同氮肥水平下丛枝菌根真菌对玉米籽粒灌浆期磷和钾吸收的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(12):3166-3178.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2022.13078
|
| [19] |
许纪东, 聂胜委, 张巧萍, 等. 旋耕方式下氮肥不同减施量对小麦产量效应的影响[J]. 山西农业科学, 2019, 47(9):1573-1576.
|
| [20] |
袁蕊, 李萍, 胡晓雪, 等. 干旱胁迫对小麦生理特性及产量的影响[J]. 山西农业科学, 2016, 44(10):1446-1449.
|
| [21] |
EVANS J R. Nitrogen and photosynthesis in the flag leaf of wheat(Triticum aestivum L.)[J]. Plant Physiology, 1983, 72(2):297-302.
doi: 10.1104/pp.72.2.297
|
| [22] |
HOU W F, TRÄNKNER M, LU J W, et al. Interactive effects of nitrogen and potassium on photosynthesis and photosynthetic nitrogen allocation of rice leaves[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1):1-13.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1600-2
|
| [23] |
ANTOLÍN M C, YOLLER J, SÁNCHEZ-DÍAZ M. Effects of temporary drought on nitrate-fed and nitrogen-fixing alfalfa plants[J]. Plant Science, 1995, 107(2):159-165.
doi: 10.1016/0168-9452(95)04108-7
|
| [24] |
VAMERALI T, SACCOMANI M, BONA S, et al. A comparison of root characteristics in relation to nutrient and water stress in two maize hybrids[J]. Plant and Soil, 2003, 255:157-167.
doi: 10.1023/A:1026123129575
|
| [25] |
HE F, SHENG M, TANG M. Effects of Rhizophagus irregularis on photosynthesis and antioxidative enzymatic system in Robinia pseudoacacia L. under drought stress[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8:183.
|
| [26] |
ROMERO-MUNAR A, DEL-SAZ N F, RIBAS-CARBÓ M, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis with Arundo donax decreases root respiration and increases both photosynthesis and plant biomass accumulation[J]. Plant,Cell and Environment, 2017, 40(7):1115-1126.
doi: 10.1111/pce.v40.7
|
| [27] |
KAMALI S, MEHRABAN A. Effects of Nitroxin and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the agro-physiological traits and grain yield of sorghum(Sorghum bicolor L.) under drought stress conditions[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(12):e0243824.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243824
|
| [28] |
FARNIA A, HADADI A. Effect of mycorrhiza and P soluble bacteria on yield and its components of maize(Zea mays L.) under water stress condition[J]. International Journal of Biology,Pharmacy and Allied Sciences, 2015, 4(10):661-674.
|
| [29] |
郑红丽, 邢杰, 胡俊, 等. 两种丛枝菌根真菌对小麦和大豆生长的影响[J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 23(1):104-106.
|
| [30] |
YE Q H, WANG H A, LI H A. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improve growth,photosynthetic activity,and chlorophyll fluorescence of Vitis vinifera L. cv. ecolly under drought stress[J]. Agronomy, 2022, 12(7):1563.
doi: 10.3390/agronomy12071563
|
| [31] |
MA S P, BI Y L, ZHANG Y X, et al. Thermal infrared imaging study of water status and growth of arbuscular mycorrhizal soybean(Glycine max)under drought stress[J]. South African Journal of Botany, 2022, 146:58-65.
doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2021.09.037
|
| [32] |
LI F, DENG J, NZABANITA C, et al. Growth and physiological responses of perennial ryegrass to an AMF and an Epichloe endophyte under different soil water contents[J]. Symbiosis, 2019, 79(2):151-161...
doi: 10.1007/s13199-019-00633-3
|
| [33] |
BITTERLICH M, SANDMANN M, GRAEFE J. Arbuscular mycorrhiza alleviates restrictions to substrate water flow and delays transpiration limitation to stronger drought in tomato[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9:154.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00154
pmid: 29503655
|
| [34] |
王琚钢, 峥嵘, 白淑兰, 等. 外生菌根对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 生态学杂志, 2012, 31(6):1571-1576.
|
| [35] |
WANG W X, ZHANG F, CHEN Z L, et al. Responses of phytohormones and gas exchange to mycorrhizal colonization in trifoliate orange subjected to drought stress[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2017, 63(1):14-23.
doi: 10.1080/03650340.2016.1175556
|
| [36] |
SHI J C, WANG X L, WANG E T. Mycorrhizal symbiosis in plant growth and stress adaptation:From genes to ecosystems[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2023, 74:569-607.
doi: 10.1146/arplant.2023.74.issue-1
|