畜牧与饲料科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 27-32.doi: 10.12160/j.issn.1672-5190.2023.03.004
复合菌不同添加量对热研4号王草青贮饲料营养价值及发酵品质的影响
罗欢1,罗皎兰1,梁琼1,易显凤2,黄世洋1
- 1.广西大学动物科学技术学院,广西 南宁 530004
2.广西农业职业技术大学,广西 南宁 530001
Effects of Different Addition Levels of Compound Bacterial Inoculants on Nutritional Value and Fermentation Quality of Pennisetum purpureum × P. glaucum cv. Reyan No. 4 Silage
LUO Huan1,LUO Jiaolan1,LIANG Qiong1,YI Xianfeng2,HUANG Shiyang1
- 1. College of Animal Science and Technology,Guangxi University,Nanning 530004,China
2. Guangxi Vocational University of Agriculture,Nanning 530001,China
摘要:
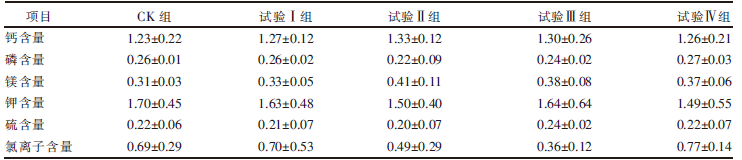
[目的]研究复合菌不同添加量对热研4号王草青贮饲料营养价值及发酵品质的影响。[方法]以调节水分至约60%的热研4号王草为试验材料,采用单因素试验设计方法,设置1个对照组(CK组)和4个试验组,每组热研4号王草重量为90 kg;CK组不添加任何菌种,试验组添加由5种青贮发酵用菌种(乳酸菌+酵母菌+枯草芽孢杆菌+地衣芽孢杆菌+植物乳杆菌)组成的不同配比的复合菌,试验Ⅰ组添加量为10 g+15 g+10 g+10 g+5 g,试验Ⅱ组添加量为10 g+15 g+15 g+15 g+10 g,试验Ⅲ组添加量为10 g+15 g+20 g+20 g+15 g,试验Ⅳ组添加量为10 g+15 g+25 g+25 g+20 g,每组重复3次;青贮发酵30 d,开袋后对各组青贮发酵产物进行质量感官评价、营养成分分析和发酵品质测定。[结果]试验Ⅰ组、Ⅲ组青贮饲料的感官评价较好,为优良等级。各组干物质含量无显著(P>0.05)差异;试验Ⅰ组的粗蛋白含量显著(P<0.05)高于试验Ⅱ组、Ⅲ组;试验Ⅰ组、Ⅱ组的淀粉含量显著(P<0.05)高于CK组以及试验Ⅲ组、Ⅳ组;试验Ⅲ组的粗灰分含量最高,显著(P<0.05)高于CK组及其他试验组;4个试验组的水溶性碳水化合物含量显著(P<0.05)高于CK组,其中,试验Ⅰ组含量最高;各组粗脂肪含量无显著(P>0.05)差异;试验Ⅲ组的总脂肪酸含量最高,显著(P<0.05)高于CK组;4个试验组的中性洗涤纤维含量显著(P<0.05)低于CK组;试验Ⅰ组、Ⅱ组的酸性洗涤纤维含量显著(P<0.05)低于试验Ⅳ组,试验Ⅲ组、Ⅳ组的酸性洗涤纤维含量显著(P<0.05)高于CK组;试验Ⅱ组的木质素含量显著(P<0.05)低于CK组;4个试验组中,试验Ⅰ组的30 h中性洗涤纤维消化率最高,试验Ⅱ组、Ⅲ组、Ⅳ组的30 h中性洗涤纤维消化率显著(P<0.05)低于CK组;各组钙、磷、镁、钾、硫元素及氯离子含量无显著(P>0.05)差异。各组乳酸、乙酸含量无显著(P>0.05)差异,试验Ⅰ组乳酸含量最高,试验Ⅳ组乙酸含量最高;试验Ⅰ组、Ⅱ组、Ⅲ组的丁酸含量显著(P<0.05)低于CK组;试验Ⅲ组的氨态氮含量显著(P<0.05)低于CK组。[结论]在调节水分至约60%的情况下,90 kg热研4号王草中添加乳酸菌10 g、酵母菌15 g、枯草芽孢杆菌10 g、地衣芽孢杆菌10 g、植物乳杆菌5 g,可以提高青贮营养价值及发酵品质。
中图分类号: