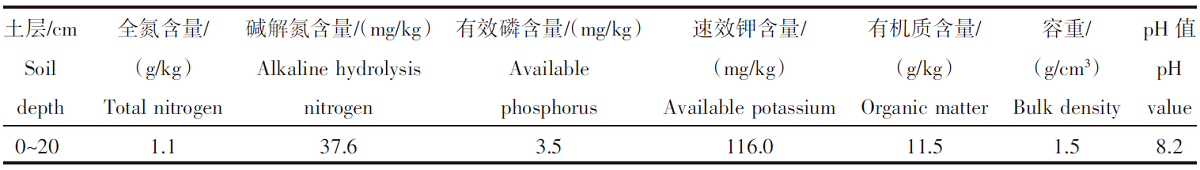
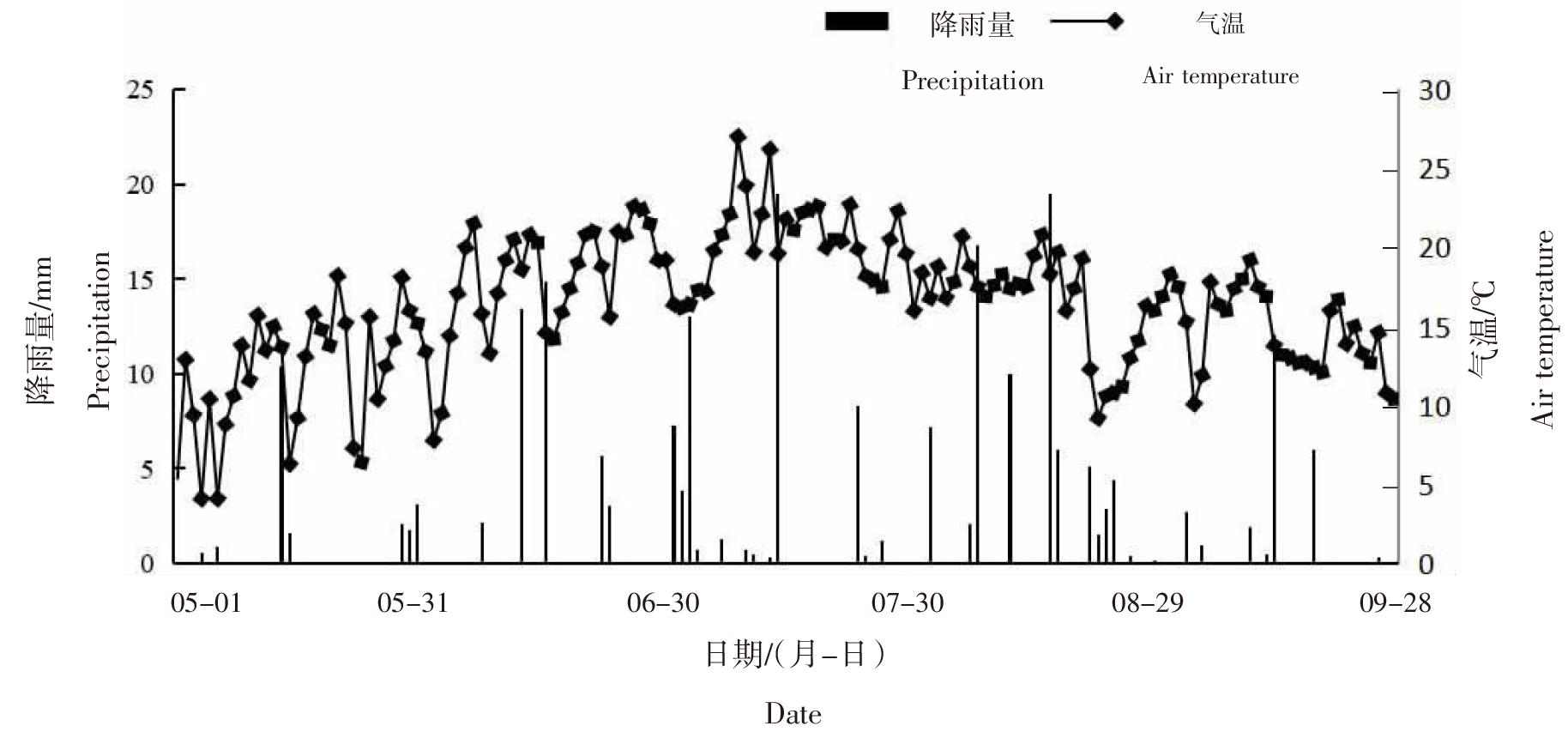
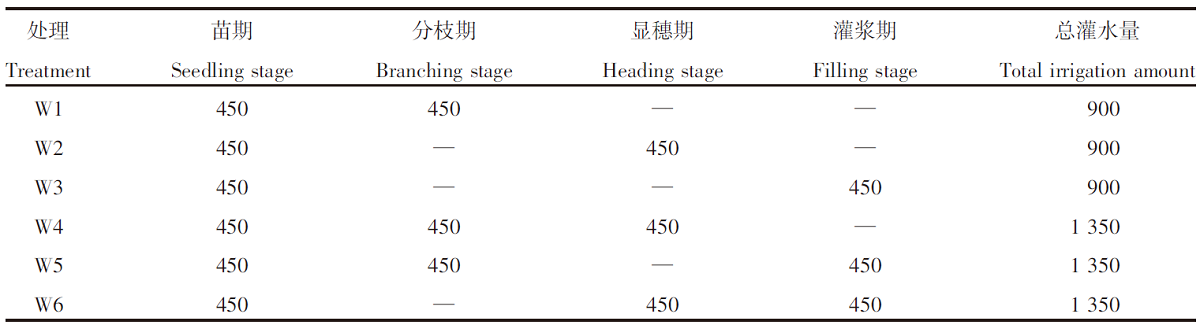
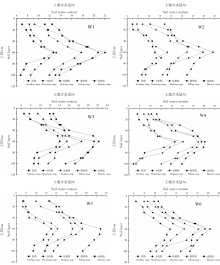
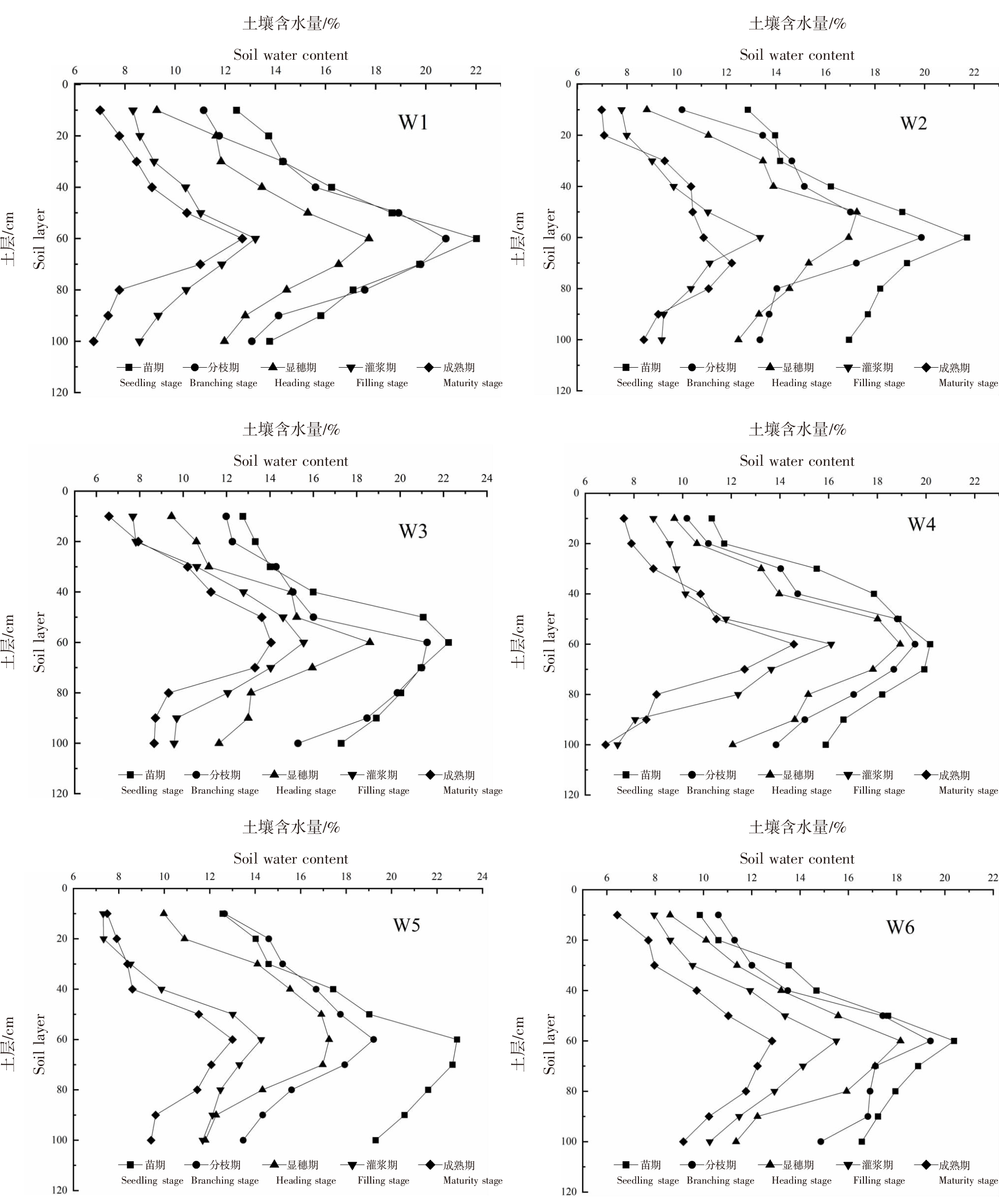
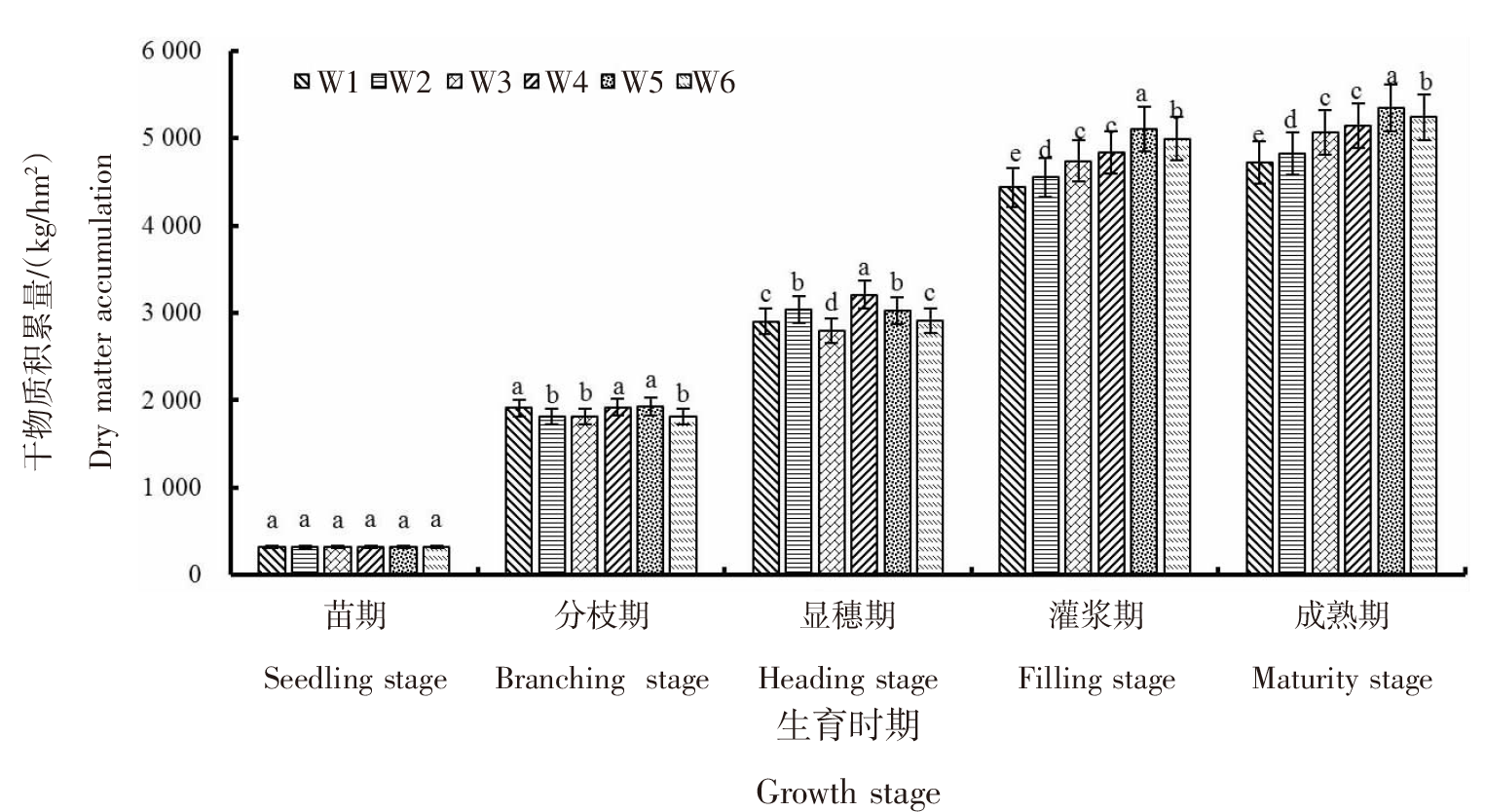
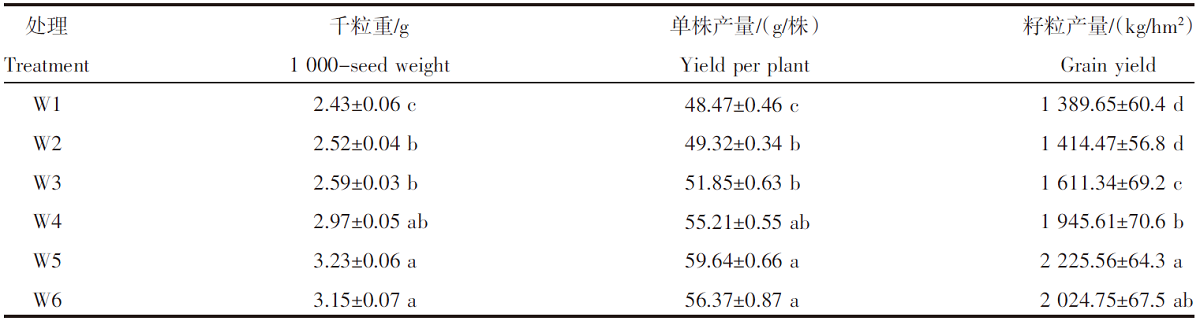
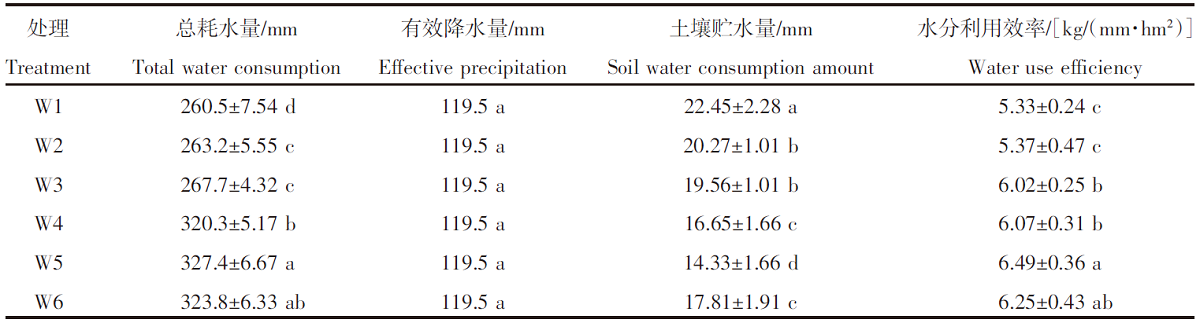
| [1] |
PEREIRA E, ENCINA-ZELADA C, BARROS L, et al. Chemical and nutritional characterization of Chenopodium quinoa Willd(quinoa) grains:A good alternative to nutritious food[J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 280:110-114.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.12.068
|
| [2] |
王晨静, 赵习武, 陆国权, 等. 藜麦特性及开发利用研究进展[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2014, 31(2):296-301.
|
| [3] |
BAZILE D, JACOBSEN S E, VERNIAU A. The global expansion of quinoa:Trends and limits[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7:622.
|
| [4] |
TALEBNEJAD R, SEPASKHAH A R. Effect of deficit irrigation and different saline groundwater depths on yield and water productivity of quinoa[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2015, 159:225-238.
doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2015.06.005
|
| [5] |
任贵兴, 杨修仕, 么杨. 中国藜麦产业现状[J]. 作物杂志, 2015(5):1-5.
|
| [6] |
KAKABOUKI I, ROUSSIS I E, PAPASTYLIANOU P, et al. Growth analysis of quinoa(Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) in response to fertilization and soil tillage[J]. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca, 2019, 47(4):1025-1036.
doi: 10.15835/nbha47411657
|
| [7] |
WALTERS H, CARPENTER-BOGGS L, DESTA K, et al. Effect of irrigation,intercrop,and cultivar on agronomic and nutritional characteristics of quinoa[J]. Agroecology and Sustainable Food Systems, 2016, 40(8):783-803.
doi: 10.1080/21683565.2016.1177805
|
| [8] |
张军瑗. 藜麦病虫害防治措施初探[J]. 种子科技, 2021, 39(24):78-79.
|
| [9] |
康文钦, 杜磊, 于利峰, 等. 阴山北麓地区降水特性和作物需水耦合关系分析:以武川县为例[J]. 北方农业学报, 2020, 48(5):83-89.
doi: 10.12190/j.issn.2096-1197.2020.05.15
|
| [10] |
LI Y, WANG J, TANG J Z, et al. Optimum planting date and cultivar maturity to optimize potato yield and yield stability in North China[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021, 269:108179.
doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2021.108179
|
| [11] |
刘文瑜, 杨发荣, 谢志军, 等. 不同品种藜麦幼苗对干旱胁迫的生理响应及耐旱性评价[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2021, 39(6):10-18.
|
| [12] |
任永峰, 王志敏, 赵沛义, 等. 内蒙古阴山北麓区藜麦生态适应性研究[J]. 作物杂志, 2016(2):79-82.
|
| [13] |
任永峰, 梅丽, 杨亚东, 等. 播期对藜麦农艺性状及产量的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(5):643-656.
|
| [14] |
任永峰, 黄琴, 王志敏, 等. 不同化控剂对藜麦农艺性状及产量的影响[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2018, 23(8):8-16.
|
| [15] |
任永峰, 黄琴, 王志敏, 等. 藜麦植株养分积累对源库调节的响应[J]. 华北农学报, 2018, 33(5):151-159.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2018.05.021
|
| [16] |
张凤珍, 张沛明, 公晓霞. 水分对农作物生长的影响[J]. 吉林农业, 2012(12):205.
|
| [17] |
姚有华, 白羿雄, 吴昆仑. 亏缺灌溉对藜麦光合特性、营养品质和产量的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2019, 28(5):713-722.
|
| [18] |
TABOADA C, MAMANI A, RAES D, et al. Farmers′ willingness to adopt irrigation for quinoa in communities of the Central Altiplano of Bolivia[J]. Revista Latinoamericana De Desarrollo Económico, 2011:7-28.
|
| [19] |
GARCIA M, RAES D, JACOBSEN S E. Evapotranspiration analysis and irrigation requirements of quinoa(Chenopodium quinoa)in the Bolivian Highlands[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2003, 60(2):119-134.
doi: 10.1016/S0378-3774(02)00162-2
|
| [20] |
齐天明, 李志坚, 秦培友, 等. 藜麦栽培技术研究与应用展望[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(3):157-165.
doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2021.0190
|
| [21] |
李晓光. 农田节水灌溉工程技术措施分析[J]. 工程技术研究, 2021, 6(7):145-146.
|
| [22] |
张岁岐, 周小平, 慕自新, 等. 不同灌溉制度对玉米根系生长及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2009, 25(10):1-6.
|