北方农业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 20-27.doi: 10.12190/j.issn.2096-1197.2023.04.03
青海东部马铃薯-土壤系统中营养元素特征研究
代璐1, 张亚峰1, 贺连珍1, 董永雯1, 秦永强2
- 1.青海省第五地质勘查院 生态环境与农业资源研究分院,青海 西宁 810099
2.海东市平安区高原富硒现代农业示范园区管理委员会,青海 海东 810600
Research on nutrient elements characteristics in potato-soil system in eastern Qinghai
DAI Lu1, ZHANG Yafeng1, HE Lianzhen1, DONG Yongwen1, QIN Yongqiang2
- 1. Research Branch of Ecological Environment and Agricultural Resources,The Fifth Geological Exploration Institute of Qinghai Province,Xining 810099,China
2. Management Committee of Plateau Selenium-rich Modern Agriculture Demonstration Zone of Ping′an District,Haidong City,Haidong 810600,China
摘要:
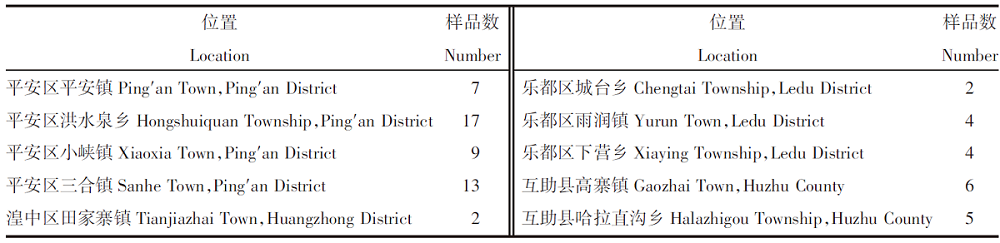
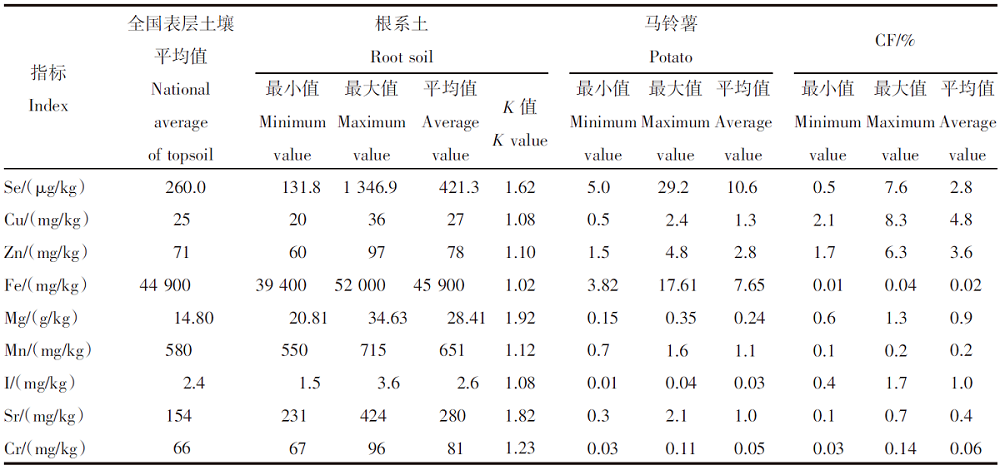
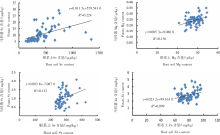
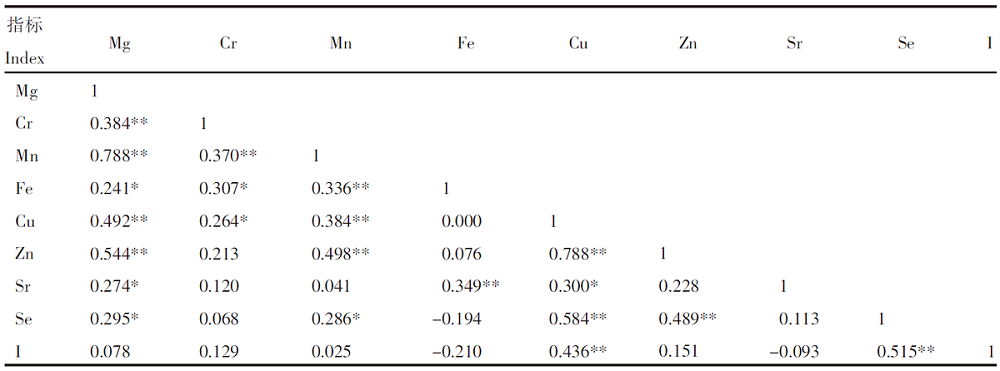
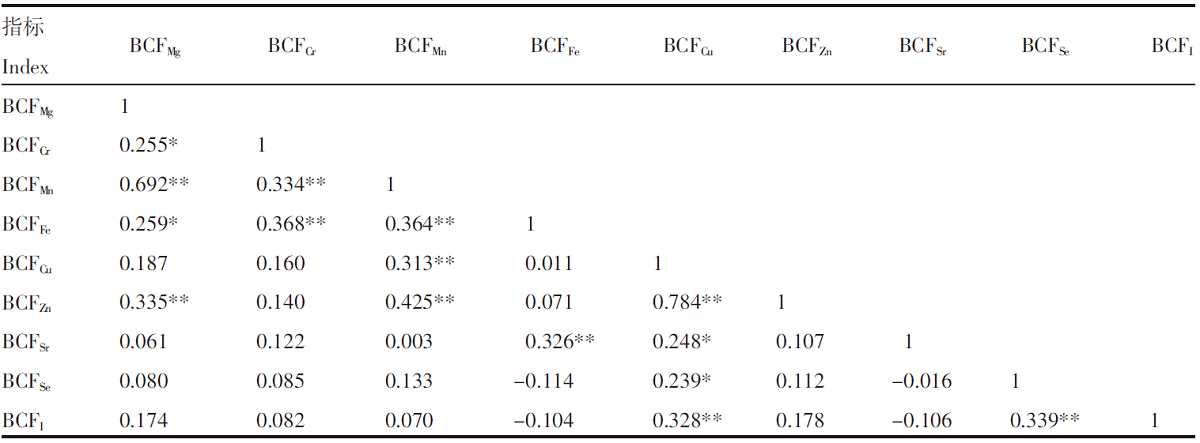
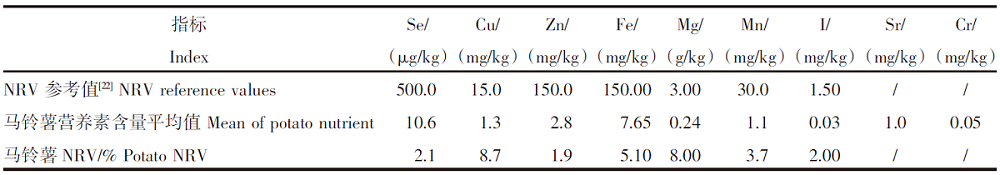
【目的】研究马铃薯-土壤系统中营养元素的含量水平,筛选高原地区马铃薯特色产品,优化马铃薯品质。【方法】对青海省东部地区马铃薯及其根系土中Se、Cu、Zn、Fe、Mg、Sr、Mn、I和Cr等营养元素进行调查分析,并利用特征参数、富集系数、相关性分析等方法,对马铃薯及其土壤环境中的营养元素水平和吸收规律进行评价。【结果】青海省东部土壤Se含量平均值为421.3 μg/kg、Cu为27 mg/kg、Zn为78 mg/kg、Fe为45 900 mg/kg、Mg为28.41 g/kg、Mn为651 mg/kg、I为2.6 mg/kg、Sr为280 mg/kg、Cr为81 mg/kg。Se、Sr、Mg、Cr显著富集,判定研究区属富硒-高锶-高镁-适铬型土壤;产出的马铃薯中Se含量平均值为10.6 μg/kg、Cu为1.3 mg/kg、Zn为2.8 mg/kg、Fe为7.65 mg/kg、Mg为0.24 g/kg、Mn为1.1 mg/kg、I为0.03 mg/kg、Sr为1.0 mg/kg、Cr为0.05 mg/kg。马铃薯富硒率为18.8%。根据马铃薯对各营养元素的富集系数强弱可判定其存在喜Cu和Zn、厌Cr和Fe的特性。根据“土壤-马铃薯”系统中元素间的相关性评价推断,马铃薯在元素吸收机理中可能存在Mg-Mn-Zn和Se-I的协同序列。【结论】青海东部具有天然特色资源优势,属富硒-高锶-高镁-适铬型土壤,可根据马铃薯的吸收机理建立富硒高镁的特色马铃薯产品。
中图分类号:
- S532